Golden Elixir: 7 Amazing Benefits Of Honey.

Often called nature’s golden elixir, honey has been valued for centuries not only for its sweet taste but also for its countless health benefits. Besides being a delicious addition to our diet, honey has several medicinal properties that make it a true superfood. In this article, you will learn about seven amazing benefits of honey that show why it deserves a prominent place in our daily lives.

7 Amazing Benefits of The Golden Elixir, Honey.
1. Powerful antioxidant:
The Golden Elixir, honey is rich in antioxidants, including phenolic compounds and flavonoids. These antioxidants help fight oxidative stress in the body by neutralizing harmful free radicals that can contribute to a variety of chronic diseases and premature aging. Consuming honey regularly can help boost your immune system and overall well-being.
2. Wound healing and antibacterial properties:
One of the oldest uses of the golden elixir, honey is to treat wounds. Its natural antibacterial properties due to the presence of hydrogen peroxide and other bioactive compounds make it an effective wound healing agent. Applying honey topically can help prevent infections, reduce inflammation, and promote faster tissue regeneration.
3. Soothes cough and sore throat:
Honey, the golden elixir has long been a popular remedy for soothing coughs and relieving sore throats. The thick consistency forms a protective film on the throat, relieving irritation and providing relief. Plus, honey’s antibacterial properties help fight the root cause of respiratory infections, making it a natural and delicious alternative to regular cough syrup.

4. Increase natural energy:
For a quick and natural energy boost,the golden elixir, honey is a great choice. The natural sugars in honey (mainly fructose and glucose) provide a quick source of energy, making it an ideal pre-workout snack. Unlike refined sugar, honey contains trace vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help maintain energy levels without the energy crash associated with processed sugar.
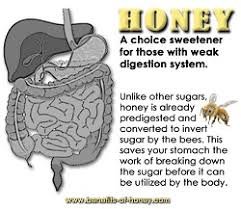
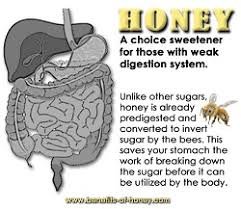
5. Digestive Health:
The golden elixir, honey can play a positive role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. It has prebiotic properties that promote the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut. This, in turn, helps maintain a healthy microbial balance and promotes improved digestion and nutrient absorption. Some people include honey in their diet to relieve digestive problems such as indigestion and bloating.
6. Skin Care Elixir:
When applied topically, the golden elixir, honey can do wonders for your skin. Its moisturizing and moisturizing properties help retain moisture, making it an effective natural treatment for dry skin. Honey’s antibacterial properties make it a valuable ingredient in skin care products, helping prevent and treat acne. Honey masks or skin care products containing honey can help achieve a healthy, glowing complexion.
7. Cardiovascular Health:
Studies suggest that regular consumption of honey may have positive effects on cardiovascular health. The antioxidants in honey, along with its ability to improve cholesterol levels, contribute to reducing the risk of heart disease. Additionally, honey may help lower blood pressure, making it a heart-friendly sweetener when used in moderation.

As we uncover the diverse benefits of honey, it becomes evident that this natural sweetener is more than just a delightful addition to our culinary creations. From antioxidant-rich properties to wound healing capabilities, honey stands as a versatile and holistic health enhancer. Using the golden elixir in your daily life can be an enjoyable step toward overall wellness and a healthy lifestyle.

The Golden Elixir: Unraveling The Intricate Process of Honey Production.
Honey, that golden elixir gracing our tables, is not just a sweet delight; it’s the result of a fascinating alchemical process orchestrated by nature’s most industrious creatures – bees. The journey from flower nectar to the jar on our kitchen shelves is a complex and collaborative effort, involving the diligent work of honeybees and the transformative magic of enzymatic activity. In this essay, we will explore the intricate process of honey production, shedding light on the remarkable journey of nectar to honey.
Collection of Nectar:
The journey begins with the foraging worker bees, equipped with specialized mouthparts designed to suck nectar from flowers. Nectar, a sugary liquid produced by flowers to attract pollinators, serves as the raw material for honey. Bees visit flowers in search of nectar, using their proboscis to extract this sweet liquid from the flower glands. Amazingly, a single bee can visit thousands of flowers in a day and collect a small amount of nectar from each flower.

Shipping and handling:
After collecting the golden elixir, honey, foraging bees return to the hive with their precious cargo. The honey is stored temporarily on top of the honey where enzymes are infused. The process begins with the conversion of complex sugars into simple sugars, such as glucose and fructose, and begins the conversion of nectar into the golden elixir, honey. Enzymes like invertase play a crucial role in breaking down these sugars, making the nectar more digestible for the bees.
Deposit in Honeycomb Cells:
Back at the hive, worker bees transfer the partially processed nectar to younger worker bees. These younger bees continue the process of honey-making by further breaking down the sugars and depositing the nectar into hexagonal wax cells within the honeycomb. The hexagonal shape of the cells maximizes storage efficiency and minimizes the amount of wax required for construction.
Evaporation and Dehydration:
The magic of honey production lies in the dehydration process that follows. Worker bees blow into the hive cells with their wings, creating an air current that helps evaporate water from the honey. Reducing moisture content is very important for honey preservation because lower moisture content inhibits microbial growth. Bees diligently maintain optimal conditions for honey production, reducing the water content of honey to approximately 17-20%.
Aging and Sealing:
As the golden elixir, honey matures into honey, its chemical composition undergoes significant changes. Acidity increases and enzymes continue to break down complex sugars into simple sugars. The ripening process contributes to the development of the unique taste, aroma and viscosity of the final honey product. Once the honey reaches the desired consistency and moisture content, the bees coat the honeycomb cells with beeswax, sealing the precious honey inside.
Beekeeper’s Harvest:
Beekeepers notice signs of ripe honey and carefully collect honeycomb frames from the hive. Modern beekeeping practices prioritize sustainability, leaving bees with enough honey to thrive during the winter. The collected honeycomb frames are then removed using centrifugal force to separate the honey from the honeycomb.

Filtration and Bottling:
Once extracted, the honey is filtered to remove any remaining impurities and wax particles. This makes the honey pure and transparent. The final step involves bottling the honey and making it ready for consumption by consumers around the world. The different flavors and colors of honey reflect the different flower fields that bees visit during their foraging expeditions.
The journey from flower nectar to the sweet golden honey on our tables is a testament to the incredible collaboration between bees and nature. The complex honey production process, which involves careful foraging, enzyme modification and careful hive management, results in a product that not only delights our taste buds but also demonstrates the extraordinary intelligence and cooperation within the hive.
Let us savor the sweetness of honey and appreciate the complex and fascinating alchemy that this golden elixir brings to our lives.















